Redis(Pub/Sub)로 로컬 캐시 동기화하기
대규모 트래픽이 발생하는 Stateless 애플리케이션 웹 서버를 운영할 때 낮은 레이턴시와 데이터베이스 부하 감소를 위해 캐시는 필수적으로 사용된다.
웹 서버에 빠르고 손 쉽게 캐시를 추가하는 방법은 로컬 인메모리 캐시를 추가하는 것이다. 하지만 대부분의 웹서버는 수많은 인스턴스로 운영되며 캐시되는 데이터가 수정될 때 모든 인스턴스의 로컬 캐시에 동기화하여야 한다.
이런 문제를 해결하기 위해, 흔히 Redis와 같은 캐시 서버를 사용할 수 있다. Redis 서버에 데이터를 캐시한다면 데이터가 변경될 때 Redis 캐시만 업데이트하면 되기 때문에 캐시 동기화 문제가 해결된다.
하지만 Redis에 캐시 데이터를 보관할 만큼의 여력이 없거나(대표적으로 비용), Redis도 결국 네트워크 지연을 피할 순 없으므로 매우 낮은 레이턴시가 요구된다면 로컬 캐시 사용이 필요할 수 있다.
로컬 캐시를 사용할 때 캐시 동기화를 위해 Redis Pub/Sub를 사용하면 모든 인스턴스에 캐시 동기화를 손쉽게 구현할 수 있다.
먼저 Redis Pub/Sub에 대해서 알아보자.
# Redis Pub/Sub
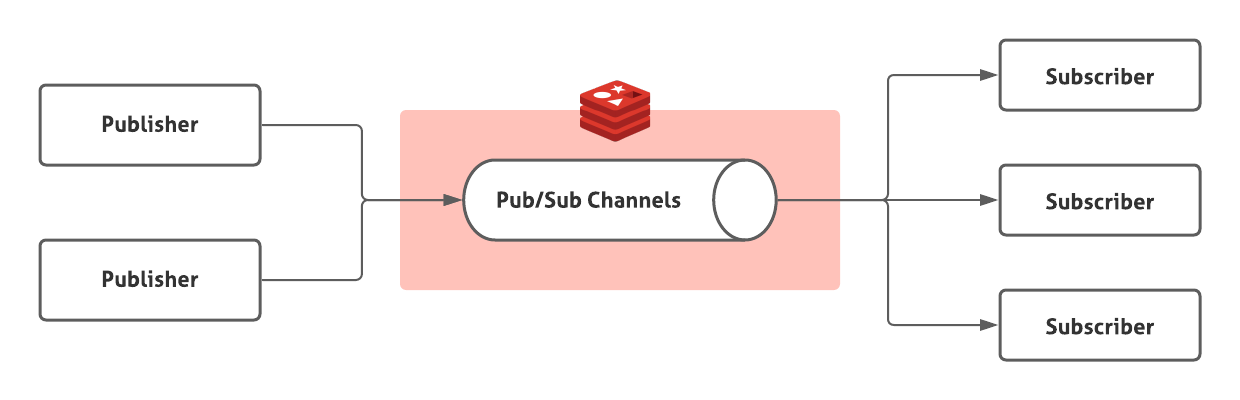
Redis Pub/Sub는 Publisher가 지정된 channel에 메시지를 보내면 해당 채널을 구독하고 있는 모든 Subscriber에게 해당 메시지를 전달해준다.
클라이언트는 여러 channel을 동시에 구독하여 관심있는 채널의 메시지들을 전달받을 수 있고 publisher 또한 여러개 존재할 수 있다.
Publisher와 Subscriber는 서로를 모르고 중앙의 Redis Pub/Sub channel을 통해서만 메시지를 주고 받는다.
Kafka와 구조는 동일하지만 메시지를 따로 저장하지 않고, 구독한 모든 Subscriber들에게 메시지가 전달되는(Kafka는 동일 컨슈머 그룹에 여러 컨슈머가 동일 토픽을 구독하면 한 컨슈머에게만 메시지가 전달된다.) 등의 차이점이 있다.
# 로컬 캐시 동기화
웹 애플리케이션 서버 3대를 운영중이라고 해보자. 각 서버는 아이템을 캐시하고 있다. 아이템의 가격이 수정될 때 모든 서버의 로컬 캐시를 무효화하여 다시 데이터베이스에서 가져와 동기화할 수 있도록 해보자.
자바 기반 프로젝트이고 실제로 웹 서버를 띄우진 않고 간단히 테스트 코드를 통해 확인을 진행한다.
# 프로젝트 세팅
plugins {
id 'java'
}
group 'org.example'
version '1.0-SNAPSHOT'
repositories {
mavenCentral()
}
dependencies {
implementation 'io.lettuce:lettuce-core:6.1.5.RELEASE'
implementation 'com.google.guava:guava:31.0.1-jre'
implementation'org.slf4j:slf4j-simple:1.7.32'
compileOnly 'org.projectlombok:lombok:1.18.22'
annotationProcessor 'org.projectlombok:lombok:1.18.22'
testImplementation 'org.assertj:assertj-core:3.21.0'
testImplementation 'org.junit.jupiter:junit-jupiter-api:5.8.2'
testRuntimeOnly 'org.junit.jupiter:junit-jupiter-engine:5.8.2'
}
test {
useJUnitPlatform()
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
- Redis 클라이언트 라이브러리로
lettuce를 사용하고 로컬 캐시 라이브러리는guava를 사용한다. 편의를 위해 lombok, assertj도 추가하였다.
# 기반 클래스 정의
import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
import lombok.Getter;
@Getter
@AllArgsConstructor
public class Item {
private Long id;
private String name;
private int price;
public void updatePrice(int newPrice) {
this.price = newPrice;
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Optional;
import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap;
public class ItemRepository {
private final Map<Long, Item> store = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
public void saveItem(Item item) {
store.put(item.getId(), new Item(item.getId(), item.getName(), item.getPrice()));
}
public Optional<Item> getItem(Long id) {
return Optional.ofNullable(store.get(id))
.map(item -> new Item(item.getId(), item.getName(), item.getPrice()));
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
- 가격을 수정할 수 있는
Item, 데이터베이스 역할을 하는ItemRepository를 정의한다.
# 캐시가 동기화가 되지 않을 때(without Redis Pub/Sub)
import com.google.common.cache.Cache;
import com.google.common.cache.CacheBuilder;
import java.time.Duration;
import java.util.Optional;
public class ItemService {
private final Cache<Long, Item> cache;
private final ItemRepository repository;
public ItemService(ItemRepository repository) {
this.cache = CacheBuilder.newBuilder()
.expireAfterWrite(Duration.ofSeconds(1))
.build();
this.repository = repository;
}
public void addItem(Item item) {
repository.saveItem(item);
cache.put(item.getId(), item);
}
public void updateItemPrice(Long id, int price) {
Item item = repository.getItem(id)
.orElseThrow(() -> new IllegalArgumentException("cannot find item. id: " + id));
item.updatePrice(price);
addItem(item);
}
public Item getItem(Long id) {
Item itemFromCache = cache.getIfPresent(id);
if (itemFromCache == null) {
Optional<Item> itemFromDB = repository.getItem(id);
itemFromDB.ifPresent(item -> cache.put(item.getId(), item));
return itemFromDB.orElseThrow(() -> new IllegalArgumentException("cannot find item. id: " + id));
}
return itemFromCache;
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
- 로컬 캐시를 사용하는
ItemService를 정의한다. 로컬 캐시는 1초후에 만료되며 ItemService는 Item을 추가, Item 가격을 수정, Item을 조회하는 기능을 제공한다. - Item을 추가하거나 Item 가격을 수정할 때 로컬 캐시에 아이템을 추가한다.
- Item을 조회할 땐 먼저 로컬 캐시에 데이터가 존재하는지 확인하고, 캐시에 없는 경우 DB에서 아이템을 조회한다.
- ItemService 인스턴스 하나가 하나의 Server가 된다.
# 테스트
import org.junit.jupiter.api.DisplayName;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import static org.assertj.core.api.Assertions.assertThat;
class ItemServiceTest {
@Test
@DisplayName("Item 가격이 수정될 때 캐시 만료 시간 전 까진 Item을 수정한 서버에서만 수정된 가격이 제공된다.")
void localCacheInvalidationTest() throws Exception {
ItemRepository repository = new ItemRepository();
ItemService serviceForServer1 = new ItemService(repository);
ItemService serviceForServer2 = new ItemService(repository);
ItemService serviceForServer3 = new ItemService(repository);
Item item1 = new Item(1L, "item1", 5000);
serviceForServer1.addItem(item1);
assertThat(serviceForServer1.getItem(item1.getId()).getPrice()).isEqualTo(5000); // check item & store item to local cache(server1)
assertThat(serviceForServer2.getItem(item1.getId()).getPrice()).isEqualTo(5000); // check item & store item to local cache(server2)
assertThat(serviceForServer3.getItem(item1.getId()).getPrice()).isEqualTo(5000); // check item & store item to local cache(server3)
serviceForServer1.updateItemPrice(1L, 3000); // update item price in server1
assertThat(serviceForServer1.getItem(item1.getId()).getPrice()).isEqualTo(3000); // updated price(server1)
assertThat(serviceForServer2.getItem(item1.getId()).getPrice()).isEqualTo(5000); // not updated price(server2)
assertThat(serviceForServer3.getItem(item1.getId()).getPrice()).isEqualTo(5000); // not updated price(server3)
Thread.sleep(2000); // wait for cache invalidation
assertThat(serviceForServer1.getItem(item1.getId()).getPrice()).isEqualTo(3000); // updated price(server1)
assertThat(serviceForServer2.getItem(item1.getId()).getPrice()).isEqualTo(3000); // updated price(server2)
assertThat(serviceForServer3.getItem(item1.getId()).getPrice()).isEqualTo(3000); // updated price(server3)
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
- server1에서 가격을 수정하고 모든 서버에서 가격을 확인하면 server1에서만 수정된 가격이 제공된다.
- 캐시가 만료된 후에는 server2, server3도 DB에서 다시 아이템을 가져오기 때문에 수정된 가격이 제공된다.
# 캐시가 동기화될 때(with Redis Pub/Sub)
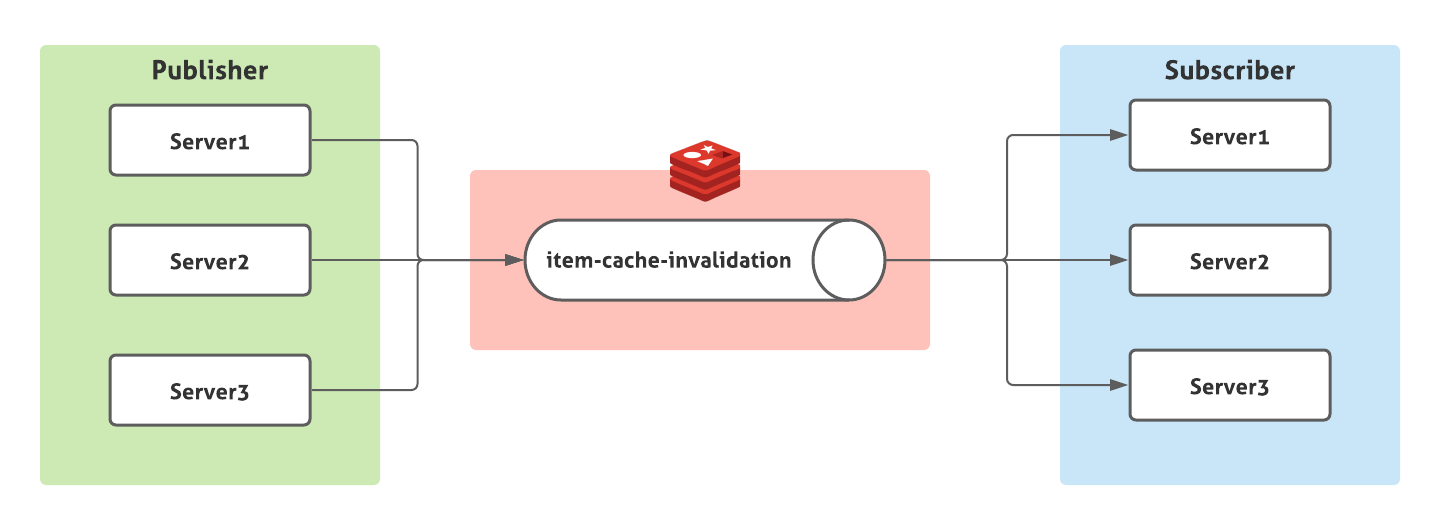
모든 서버는 item-cache-invalidation channel을 구독하는 Subscriber이면서 또한 아이템 가격이 수정될 때 해당 channel에 메시지를 보내는 Publisher가 된다.
import com.google.common.cache.Cache;
import com.google.common.cache.CacheBuilder;
import io.lettuce.core.RedisClient;
import io.lettuce.core.pubsub.RedisPubSubAdapter;
import io.lettuce.core.pubsub.api.sync.RedisPubSubCommands;
import java.time.Duration;
import java.util.Optional;
import java.util.function.Consumer;
public class ItemServiceWithPubSub {
public static final String CHANNEL = "item-cache-invalidation";
private final Cache<Long, Item> cache;
private final ItemRepository repository;
private final Consumer<Long> cacheInvalidationMessagePublisher;
public ItemServiceWithPubSub(ItemRepository repository, RedisClient client) {
this.cache = CacheBuilder.newBuilder().expireAfterWrite(Duration.ofSeconds(1)).build();
this.repository = repository;
RedisPubSubCommands<String, String> connectionForSub = client.connectPubSub().sync();
connectionForSub.getStatefulConnection()
.addListener(new RedisPubSubAdapter<>() { // 캐시를 만료시키는 리스너 추가
@Override
public void message(String channel, String message) {
cache.invalidate(Long.parseLong(message));
}
});
connectionForSub.subscribe(CHANNEL); // 해당 채널을 구독
RedisPubSubCommands<String, String> connectionForPub = client.connectPubSub().sync();
// 캐시 무효화 메시지를 전송하는 Publsuher 추가
this.cacheInvalidationMessagePublisher = id -> connectionForPub.publish(CHANNEL, id.toString());
}
public void addItem(Item item) {
repository.saveItem(item);
cache.put(item.getId(), item);
}
public void updateItemPrice(Long id, int price) {
Item item = repository.getItem(id).orElseThrow(() -> new IllegalArgumentException("cannot find item. id: " + id));
item.updatePrice(price);
addItem(item);
cacheInvalidationMessagePublisher.accept(id); // cache invalidation message 전송
}
public Item getItem(Long id) {
Item itemFromCache = cache.getIfPresent(id);
if (itemFromCache == null) {
Optional<Item> itemFromDB = repository.getItem(id);
itemFromDB.ifPresent(item -> cache.put(item.getId(), item));
return itemFromDB.orElseThrow(() -> new IllegalArgumentException("cannot find item. id: " + id));
}
return itemFromCache;
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
- 생성자에서 리스너를 추가하고 해당 channel을 구독하고 아이템 가격 수정 시 해당 channel에 메시지를 전송할 수 있는 publisher를 추가하였다.
- 아이템 가격이 수정될 때 publusher를 통해 itemId를 발행한다. 그러면 생성자에서 등록한 리스너에서 해당 메시지를 전달받아 로컬 캐시를 무효화 한다.
# 레디스 실행
# with brew
## redis 설치
brew install redis
## start redis
brew services start redis
------------------------------------
# with docker
docker run --rm -p 6379:6379 redis
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
# 테스트
import io.lettuce.core.RedisClient;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.DisplayName;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import static org.assertj.core.api.Assertions.assertThat;
class ItemServiceWithPubSubTest {
@Test
@DisplayName("Item 가격이 수정되면 모든 서버에서 수정된 가격이 제공된다.")
void localCacheInvalidationTest() throws Exception {
ItemRepository repository = new ItemRepository();
RedisClient client = RedisClient.create("redis://localhost");
ItemServiceWithPubSub serviceForServer1 = new ItemServiceWithPubSub(repository, client);
ItemServiceWithPubSub serviceForServer2 = new ItemServiceWithPubSub(repository, client);
ItemServiceWithPubSub serviceForServer3 = new ItemServiceWithPubSub(repository, client);
Item item1 = new Item(1L, "item1", 5000);
serviceForServer1.addItem(item1);
assertThat(serviceForServer1.getItem(item1.getId()).getPrice()).isEqualTo(5000); // check item & store item to local cache(server1)
assertThat(serviceForServer2.getItem(item1.getId()).getPrice()).isEqualTo(5000); // check item & store item to local cache(server2)
assertThat(serviceForServer3.getItem(item1.getId()).getPrice()).isEqualTo(5000); // check item & store item to local cache(server3)
serviceForServer1.updateItemPrice(1L, 3000);
Thread.sleep(10); // wait for redis pub/sub
assertThat(serviceForServer1.getItem(item1.getId()).getPrice()).isEqualTo(3000); // updated price(server1)
assertThat(serviceForServer2.getItem(item1.getId()).getPrice()).isEqualTo(3000); // updated price(server2)
assertThat(serviceForServer3.getItem(item1.getId()).getPrice()).isEqualTo(3000); // updated price(server3)
Thread.sleep(2000); // wait for cache invalidation
assertThat(serviceForServer1.getItem(item1.getId()).getPrice()).isEqualTo(3000); // updated price(server1)
assertThat(serviceForServer2.getItem(item1.getId()).getPrice()).isEqualTo(3000); // updated price(server2)
assertThat(serviceForServer3.getItem(item1.getId()).getPrice()).isEqualTo(3000); // updated price(server3)
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
- 아이템 가격을 수정하고 모든 서버에서 아이템을 조회하면 즉시 수정된 가격이 제공되는 것을 확인 할 수 있다.
# Publihser, Subscriber 커넥션 분리?
public ItemServiceWithPubSub(ItemRepository repository, RedisClient client) {
this.cache = CacheBuilder.newBuilder().expireAfterWrite(Duration.ofSeconds(1)).build();
this.repository = repository;
RedisPubSubCommands<String, String> connectionForSub = client.connectPubSub().sync();
connectionForSub.getStatefulConnection()
.addListener(new RedisPubSubAdapter<>() { // 캐시를 만료시키는 리스너 추가
@Override
public void message(String channel, String message) {
cache.invalidate(Long.parseLong(message));
}
});
connectionForSub.subscribe(CHANNEL); // 해당 채널을 구독
RedisPubSubCommands<String, String> connectionForPub = client.connectPubSub().sync();
// 캐시 무효화 메시지를 전송하는 Publsuher 추가
this.cacheInvalidationMessagePublisher = id -> connectionForPub.publish(CHANNEL, id.toString());
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
ItemServiceWithPubSub생성자 코드를 보면 Publisher와 Subscriber를 각각 새로운 레디스 커넥션으로 사용하는 것을 알 수 있다.- 그 이유는 Subscriber 커넥션은 Subscriber와 관련된 명령어 이외에 다른 Redis 명령어를 사용할 수 없도록 되어있기 때문이다.
- lettuce의 경우 Subscriber 커넥션에서 다른 Redis 명령어를 실행하면 예외가 발생한다.(
io.lettuce.core.RedisException: Command GET not allowed while subscribed. Allowed commands are: [PSUBSCRIBE, QUIT, PUNSUBSCRIBE, SUBSCRIBE, UNSUBSCRIBE, PING]) - Subscriber 커넥션에서 다른 명령어를 사용할 수 없는 이유는 구독된 channel에서 들어오는 메시지를 기다리는 동안 해당 커넥션은 블럭되기 때문으로 보여진다.(참고 (opens new window))
- lettuce의 경우 Subscriber 커넥션에서 다른 Redis 명령어를 실행하면 예외가 발생한다.(
- Publihser의 경우 이러한 제약이 없기 때문에 커넥션 풀을 사용하도록 개선할 수 있다.
# 레디스 클러스터에서 Pub/Sub는 어떻게 동작할까?
- 각 레디스 서버들은 channel별 subscriber들의 정보를 가지고 있고 특정 channel에 메시지가 publish되면 요청을 받은 레디스 서버는 모든 노드에게 동일한 메시지를 publish하기 때문에 레디스 클러스터에서 Pub/Sub는 아무 노드에서나 subsribe, publish를 해도 동일하게 동작한다.
- 자세한 내용은 Redis Cluster 에서의 Pub/Sub은 어떻게 동작할까? (opens new window)를 참고하자.
- 해당 특성때문에 레디스 클러스터 모드에서 샤드 수가 많은 경우 성능 이슈가 발생할 수 있어(참고 (opens new window)) 수평확장이 어려울 수 있다.
- 그래서 레디스 7이후 부터는 샤드별로 Pub/Sub 채널을 분리하는 Sharded Pub/Sub (opens new window)가 도입되었다.
# 패턴 매칭
Redis Pub/Sub는 패턴 매칭 기반으로 subscribe, publish 하는 기능도 제공한다. 자세한 내용은 공식 문서 (opens new window)를 참고하자.
